CBD vs THC - Difference Between CBD and THC Explained
When looking at the specifications of cannabis seeds in our catalog, you may often notice references to high or low levels of THC and CBD.
If you are new to the wonderful world of weed, you may be confused about what these abbreviations stand for.
And even if you are an experienced grower, there may still be some common misconceptions concerning the two terms. This article will explain all the differences between CBD flower vs THC flower to help you choose the right strain for your needs.
THC and CBD are often compared to each other, the most visible difference being that the first induces psychoactive effects and the second does not. However, the reality is somewhat more complex. But, beyond their effects, what are the differences between THC and CBD?
CBD vs THC: what are the differences?
- Difference in chemical structure
- How it affects the body
- The difference in effects
- Difference in legality
- Growing CBD vs THC
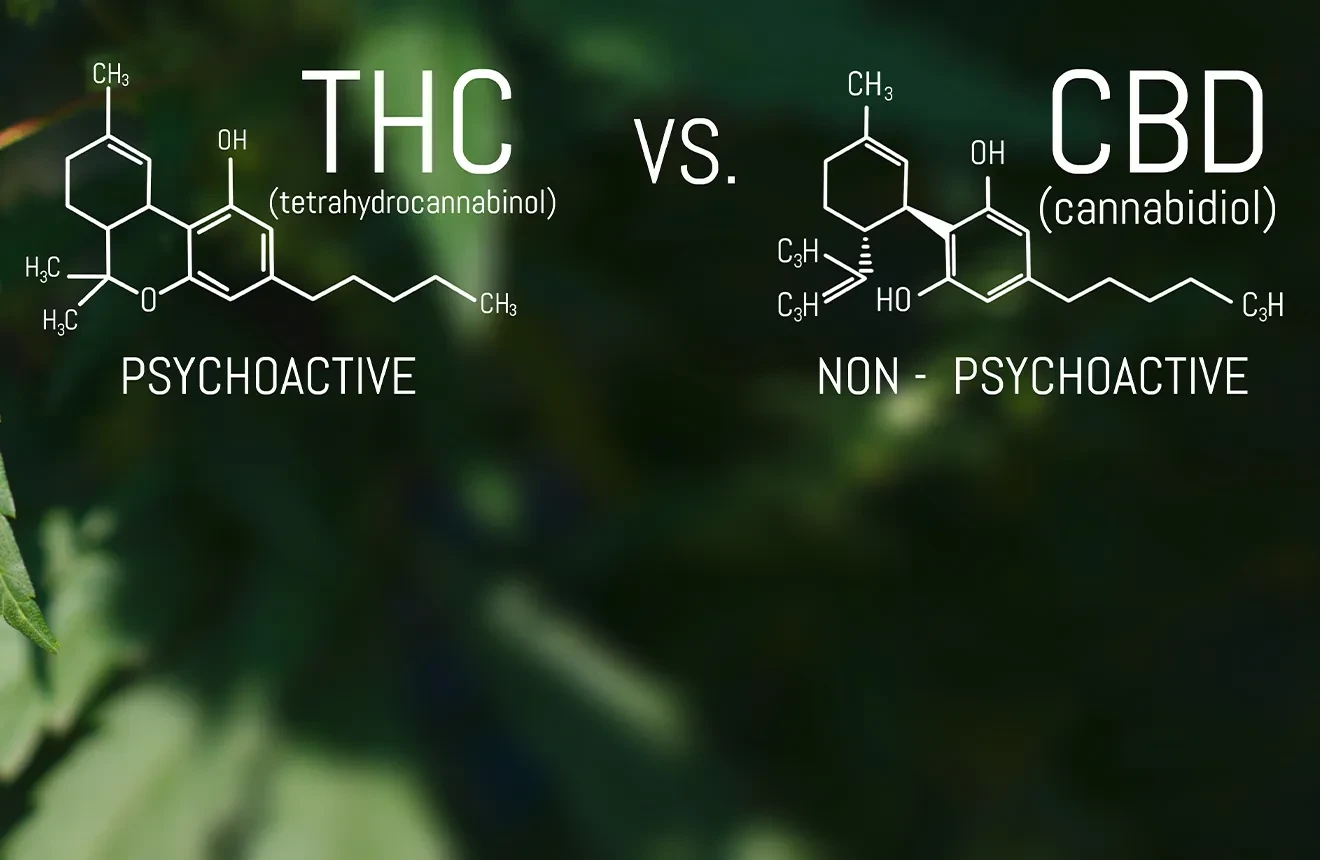
CBD vs THC: Differences in chemical structure
THC and CBD are two cannabinoids, chemical compounds secreted by cannabis plants. They are not the only cannabinoids, as researchers have identified over a hundred natural chemical compounds. Yet they are the cannabinoids that are the most talked about when it comes to cannabis and medicine. The full scientific name of THC is delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, while CBD is short for cannabidiol.
These molecules have the particularity to imitate the effects of certain chemical compounds that our body produces naturally, called endocannabinoids, and to activate our internal health systems. Endocannabinoids bind to receptors and affect sleep, pain, appetite, mood, and many other functions. Simply put, cannabinoids act as intermediaries between cells, to fight against deficiencies in our endocannabinoid system.
Cannabinoids derived from cannabis are referred to as exogenous cannabinoids, as the human body does not produce them. When consumed, cannabinoids seek to bind to receptors in our bodies. Each cannabinoid has different effects depending on which receptor it targets. For example, THC targets receptors in the brain, while CBD prefers receptors located in our bodies.
CBD and THC have the same chemical formula: 21 carbon atoms, 30 hydrogen atoms, and two oxygen atoms. Their difference lies in the way the atoms are arranged. This tiny difference gives CBD and THC different chemical properties and is also the reason why they affect the human body differently.
CBD vs THC: How it affects the body
CBD and THC both work in conjunction with receptors in the endocannabinoid system, the two main ones being the CB1 and CB2 receptors. THC binds securely to cannabinoid CB1 receptors, while CBD has a low affinity for these CB1 receptors.
To give a visual image, imagine cannabinoids as the keys to a lock. The THC molecule is perfectly formed to snap into CB1 receptors. When this connection occurs, THC activates or stimulates these CB1 receptors. THC is known as a CB1 receptor agonist.
THC partially imitates a neurotransmitter naturally produced by the human body: anandamide, which is also referred to as "the molecule of happiness".
Anandamide is an endocannabinoid that activates the CB1 receptors. Research on animal studies revealed that anandamide can increase appetite and improve pleasure associated with food consumption.
It is probably responsible for some of the rewarding effects of exercise (for example, the endorphin rush, popularly known as the runner's high). Anandamide also plays a role in memory, motivation, and pain. THC is a "key" that resembles anandamide so much that it activates or 'unlocks' the CB1 receptors, permitting it to produce these same feelings of happiness.
CBD, on the other hand, is not suitable for CB1. It is classified as a CB1 receptor antagonist. It thus does not act directly on the CB1 receptors, and further suppresses the possibilities of activation of the CB1 receptors by cannabinoids such as THC.
In other words, when you ingest THC and CBD, THC directly stimulates the CB1 receptors, while CBD counteracts the action of THC at the CB1 receptor, thereby inhibiting the psychoactive effects of THC.
CBD vs THC: Difference in effects
When it comes to recreational usage, the biggest difference between CBD and THC is the psychoactive high. While CBD can help you relax after a hard day, you will not feel that typical rush to the head and body, you usually experience after consuming THC heavy weed.
THC is not the only active compound that will stimulate this high, yet when you compare a strain with high CBD and low THC vs a strain that has low CBD and high THC, this is where you will feel the difference.
If THC and CBD have different felt effects, they are also used medicinally, either separately or in conjunction, and in varying dosages depending on the pathologies.
People who take CBD products often do so for the potential medical benefits: to relieve arthritis, Crohn's disease, diabetes, or multiple sclerosis. Some also say it helps relieve anxiety, insomnia, and chronic pain caused by inflammation. Ways of consuming are CBD oil, edibles or simply smoking CBD.
CBD is generally well-tolerated, even when consumed in large quantities, although it is such a newcomer to the medical sector that longitudinal studies have not yet been carried out, and some experts think it may affect blood pressure.
THC, on the other hand, is associated with many short-term side effects, such as:
- dry mouth
- memory loss
- red eyes
- increased heart rate
- altered decision-making
- loss of coordination
For THC, it is used in countries where the use of medical marijuana is legal for neuropathic pain, Parkinson's, nausea, or against the side effects of chemotherapy, to restore appetite in sick people, or to relieve pressure glaucoma intraocular.
THC is the most popular cannabinoid and is found in the greatest amount of cannabis. The main existing cannabis varieties have been cultivated and selected for their high concentration of THC. Its psychoactive effects produce rapid euphoria. THC has been used to combat nausea, sleep disturbances and loss of appetite. Consumed in high doses, it can, however, cause anxiety and paranoia.
There is also strong evidence linking the long-term use of THC with serious psychiatric problems, especially for teenagers with brains that are still developing. Experts believe that using THC increases the likelihood of schizophrenia for this group of people, especially young males.
CBD vs THC: Difference in legality
THC is classified as a narcotic in many countries because of its harmful cognitive effects. Access is therefore restricted for medical and research purposes. CBD has lower health risks and is, therefore, legal in numerous countries, including the UK and France. This means that CBD is used far more in natural supplements sold commercially.
Growing CBD vs THC
Growing CBD seeds are not much different than growing weed seeds with high THC levels. While their effects are different, CBD plants will look very similar to 'normal' cannabis plants. Cultivating CBD seeds will also not need a different approach, so if you are already familair with growing your run of the mill autoflower seeds or photoperiod feminized seeds, you should be able to grow your own CBD weed as well. If you are a first time grower, and you would like a step-by-step guide that will lead your through the entire grow process, just check out our Grow Guide for Beginners!
What about the entourage effect?
There are countless varieties of cannabis with different effects. However, they all develop the same active ingredient: THC. In addition to THC, the Cannabis Sativa L. plant has a multitude of chemical components, 480 of which have so far been identified. If cannabinoids have undoubtedly the most important physiological effects, the terpenes responsible in particular for the taste of weed and the flavonoids responsible for the colour of the plant would also have neurochemical effects.
Little is known about the action of all of these components on the body. However, they are said to have the potential to support the effects of THC by creating a form of synergy, the so-called entourage effect. This would attest, for example, to the difference in effects between whole-plant extracts and pure, isolated cannabinoids.
What is the so-called entourage effect?
When we use cannabis, our bodies absorb hundreds of compounds. Everyone comes with unique effects and benefits, and their behavior can change in the presence of other compounds. This is the principle of the entourage effect, where 1+1 can potentially add up to 3.
For example, in a 2010 study, patients with cancer pain were given either a pure THC extract or an extract containing almost equal levels of THC and CBD. Patients who have received the THC / CBD combo reported less pain. Conversely, the entourage effect would explain why CBD alone is not necessarily the most effective.
But cannabis is much more than THC and CBD. It also produces other cannabinoids like CBN, CBC, or CBG and dozens of others, as well as terpenes. The possible synergies are multiplied by the number of compounds. Unfortunately, very few studies to date have explored these synergies in humans.
Many believe that CBD, while effective on its own, is even more beneficial with THC. Doctors often advise patients to start on low doses of products containing THC and CBD because of the associated side effects, which are so variable from patient to patient.
Scientific reality or a clever marketing strategy?
Chris Emerson, chemist and co-founder of the company that created the Level Blends, a vaporizer, believes that the entourage effect can be described as "the sum of all the parts that lead to the power or magic of cannabis". He thinks it is possible to modify the ratios of terpenes and cannabinoids of e-liquids to obtain a specific effect and possibly be able to create products personalized for the needs of the consumer or the patient.
It is also all the meaning of the breeding culture in which the smallest genetic aspects of the plant are measured and manipulated to produce different effects.
Margaret Haney, a neurobiologist specializing in cannabis research at Columbia University claims that these allegations are just a marketing strategy for business. She does not deny as a whole the existence of the entourage effect but underlines the lack of data.
Who knows where the truth lies? One thing is for sure; there is plenty we still don't know about the potential benefits of cannabis.
What exactly is full-spectrum CBD?
You may have noticed terms such as 'pure CBD' 'full-spectrum', or broad-spectrum' on the packaging of cannabis products, but what exactly does this mean?
Full-spectrum CBD means that the cannabidiol contained within the product also contains other cannabinoids, such as CBG, CBN, or CBC, or CBG, and occasionally even THC in legal proportions. It means that each part of the plant was used in the extraction, and all of the active ingredients in weed were retained in the extract.
Why is this important? Cannabinoids have been shown to have extra effects when combined together, an interaction known as the entourage effect. CBD is, in that case, "more effective".
Where does CBD isolate come in?
As the name suggests, CBD isolate is an extraction of pure CBD, often higher than 99%, completely separated from other cannabinoids. You will often find CBD isolate in the form of a crystallized powder.
Isolating an active ingredient is common in the pharmaceutical sector to optimize its efficacy and stabilize the molecule. Nevertheless, it does not consider the different potential interactions between the many complex compounds of the cannabis plant.
Which is better?
For many years, research has been restricted to the study of CBD, which allows accurate dosing, particularly for those who manufacture their own CBD products. However, more research has been done on the broader spectrum in the last few years.
Dr. S. Burstein of the University of Massachusetts stated in a 2015 research that, based on earlier research, the combination of both CBD and THC was found more effective in treating Alzheimer's disease in mice than both cannabinoids separately. They found similar results when applied to rats that were suffering conditions modeled after Huntington's disease. While mice and rats are not the same as humans, this can be an early indication, showing that full-spectrum CBD might have a better therapeutic effect than isolate CBD.
Some people, however, have little tolerance for THC, even in the tiny quantities of legal doses, or cannot risk having any trace of THC in their blood. CBD isolate can still be a good option for those in these circumstances.
What have we learned?
In short, CBD and THC are two cannabinoids, chemical compounds that interact with our bodies and brains in different ways. This is what makes us experience contrasting effects. While there are clear differences between how CBD and THC are used for recreational and medical usage, growing CBD or THC-heavy seeds do not need differing approaches.
While research on both cannabinoids is still lacking, it does seem so far that the two compounds work better together than alone. When it comes to cannabinoids, it seems like teamwork also makes the dream work.


